(TT) – Monkeypox in humans was first identified in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo
It is an infectious disease caused by monkeypox virus which is of the genus “Orthopoxvirus” in the family “Poxviridae” just like the cowpox virus and variola virus that causes smallpox. Monkeypox occurs primarily around rainforests of West and Central Africa, but the natural host of the virus is still not known.
History
Monkeypox was first identified as an illness of non-human primates. The virus is also found in rodents. Monkeypox in humans was first identified in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Democratic Republic of the Congo routinely reports a high number of cases: more than 1,000 suspected cases per year since 2005.
Through vaccination, Smallpox was eradicated in 1980 and vaccination ceased. Since then monkeypox virus emerged as the most significant orthopoxvirus in humans which is explained to be due to waning immunity from smallpox vaccines.
The subtypes of the virus are grouped in two clades; The Central African clade, which is prevalent in the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and other East African countries. The virus in this clade causes more severe illness clinically and case fatality is up to 11%.
The next subtype is the West African clade, found in Nigeria, Sierra Leone, Liberia and Côte d’Ivoire. This clade of monkeypox virus causes less human-to-human transmission. It has less severe illness, and death in up to 6% of cases.
Geographic Distribution Of Monkeypox Disease
Since 2016, Confirmation of human monkeypox has been reported since 2016 in; Central African Republic, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Democratic Republic of Congo, Nigeria and the Republic of the Congo.
Cases of the disease were reported in Israel, United Kingdom and Singapore among travelers from Nigeria.
Symptoms To Lookout For
For the onset of symptoms, the interval is usually 6 to 13 days, but can be from 5 to 21 days.
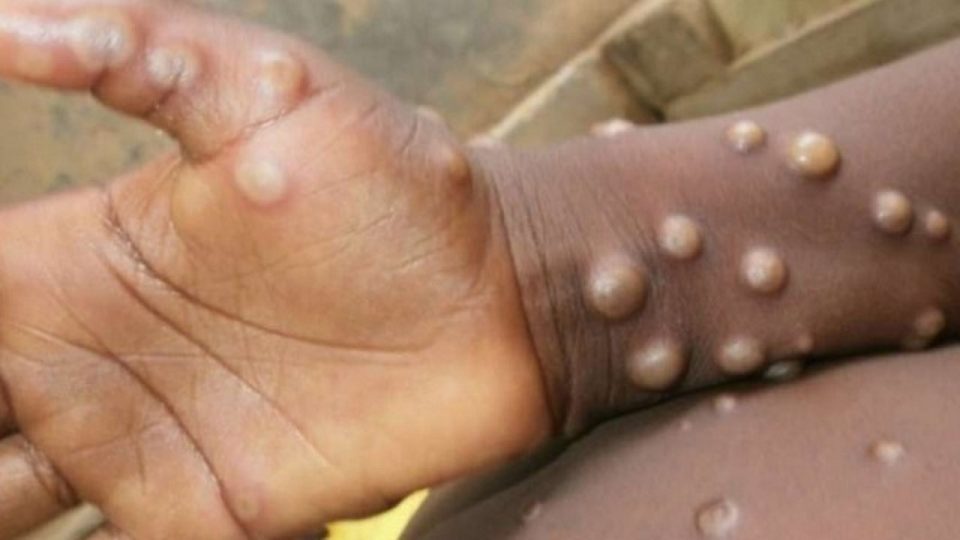
Monkeypox virus disease symptoms are very similar to that of smallpox. Smallpox disease is more severe than the monkeypox virus. If you have monkeypox, you may experience symptoms such as; severe rash which is typically self-limiting, but can lead to severe illness or death. Death in monkeypox occurs in up to 11% of cases, most often in younger age groups.
The infection progresses in two phases:
- Invasion period (0-5 days) characterized by fever, headache, lymphadenopathy (swelling of the lymph nodes), back pain, myalgia (muscle aches), and fatigue; and
- Characteristic rash appearing in stages 1-3 days after the onset of fever, beginning on the face and spreading to the trunk and limbs.
The rash lesions evolve from macules (lesions with a flat base) to papules (raised firm lesions) to vesicles (filled with clear fluid) to pustules (filled with yellowish fluid), followed by crusts.
The rash affects
- The face in 95% of cases,
- The palms and soles of the feet (75%),
- Oral mucous membranes (70%),
- Genitalia (30%),
- The conjunctivae and cornea (20%).
It may take three weeks for crusts to disappear. Lesions range from a few to several thousand and are often painful. Severe lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes) is a distinctive feature of monkeypox and generally develops before the rash. Monkeypox usually lasts 3 to 4 weeks. Severe illness occurs more commonly in children.
Transmission and Treatment
As Monkeypox is a zoonosis which means that it is transmitted to humans from animals. You can get the virus by touching or handling infected animals such as; giant poached rats, rope squirrels, and monkeys or eating inadequately cooked meat of infected animals. Human to human transmissions occur through contact with infected respiratory droplets, skin lesions, or contaminated objects.
There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, but the smallpox vaccines is confirmed to offer protection against monkeypox virus. Other treatments are supportive approaches based on one’s specific symptoms.